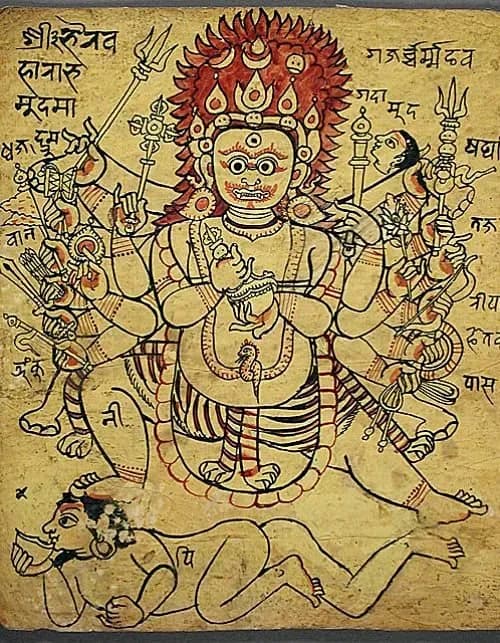
Atimarga
Overview
Atimarga is a concept in Tantric traditions of Hinduism that refers to the path of spiritual practice that goes beyond the conventional norms and restrictions of society. It is a path of radical freedom and individuality that aims at attaining enlightenment through unconventional means.
History
Atimarga has its roots in the Tantric traditions of Hinduism, which emerged in India around the 5th century CE. These traditions were characterized by their emphasis on transgressive practices, including the use of sexual rituals, consumption of intoxicants, and breaking of social norms and taboos.
The Kaula and Vama traditions of Tantra were particularly associated with Atimarga. These traditions viewed conventional morality and ethics as impediments to spiritual liberation and advocated the use of unconventional means to break free from the limitations of conventional reality.
Significance
Atimarga is significant in Tantric traditions because it challenges conventional notions of morality and ethics and offers an alternative path to spiritual liberation. It is considered to be a path of transgression that can be used to break free from the limitations of social conditioning and ego, leading to a direct experience of the divine.
However, Atimarga is not without its critics. Some scholars argue that its emphasis on transgression can lead to excess and abuse, particularly in the context of sexual rituals.
Connected Topics
Famous Quotes
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
Types and Definitions
There are several types of Atimarga, each with its own unique characteristics and practices. Here are some of the types and their definitions:
Atimarga- Shaivism
Mentioned in Books
Atimarga is a spiritual path that has been mentioned in several ancient scriptures from different traditions in India. Here are some of the main scriptures in which Atimarga is mentioned:
The Upanishads: The Upanishads are a collection of texts that form the foundation of Hindu philosophy. They contain teachings related to Atimarga, including the importance of self-inquiry, meditation, and the cultivation of wisdom.
The Bhagavad Gita: The Bhagavad Gita is a Hindu scripture that contains teachings on Atimarga, including the importance of selfless action, devotion to a higher power, and the practice of meditation and self-control.
The Yoga Sutras of Patanjali: The Yoga Sutras of Patanjali is a collection of aphorisms that outline the practice of yoga, including Atimarga. It contains teachings on meditation, concentration, and the cultivation of inner stillness and peace.
The Hatha Yoga Pradipika: The Hatha Yoga Pradipika is a text on the practice of Hatha yoga, which is a form of yoga that emphasizes physical postures and breathing exercises. It contains teachings on Atimarga, including the importance of purifying the body and mind to achieve spiritual growth and awareness.
The Vedas: The Vedas are the oldest Hindu scriptures that contain teachings related to spirituality, including Atimarga. They emphasize the importance of self-realization, the cultivation of wisdom, and the performance of selfless actions to achieve spiritual growth.
The Shiva Sutras: The Shiva Sutras are a collection of aphorisms that outline the philosophy and practices of Shaivism, a Hindu tradition that venerates Lord Shiva. They contain teachings on Atimarga, including the importance of self-realization and the practice of meditation.
The Tirumantiram: The Tirumantiram is a Tamil scripture that contains teachings on Saiva Siddhanta, a Tamil Shaiva tradition. It contains teachings on Atimarga, including the importance of self-realization, devotion, and the practice of yoga.
These are some of the main scriptures in which Atimarga is mentioned.
FAQs
Q: What is Atimarga?
A: Atimarga is a spiritual path that emphasizes the direct experience of the divine through meditation, self-inquiry, and the cultivation of wisdom. It is a path of self-realization that aims to liberate the individual from the cycle of birth and death and attain oneness with the ultimate reality.
Q: Who can practice Atimarga?
A: Anyone can practice Atimarga, regardless of their background or belief system. It is a universal spiritual path that can be practiced by people of any religion or culture.
Q: What are the practices of Atimarga?
A: The practices of Atimarga include meditation, self-inquiry, the cultivation of wisdom, and the performance of selfless actions. These practices aim to purify the mind and body, cultivate inner peace and stillness, and ultimately lead to the direct experience of the divine.
Q: What are the benefits of practicing Atimarga?
A: The benefits of practicing Atimarga include increased inner peace and clarity, a greater sense of connection with the divine, and a deeper understanding of one's true nature. It can also lead to greater compassion and selflessness, as well as a more meaningful and fulfilling life.
Q: How is Atimarga different from other spiritual paths?
A: Atimarga is a non-dualistic path that emphasizes the direct experience of the divine, rather than religious rituals or dogma. It is a path of self-realization that aims to transcend the limitations of the ego and the mind, and attain oneness with the ultimate reality.
Q: Is Atimarga a form of yoga?
A: Atimarga is often considered a form of yoga, as it includes many of the same practices, such as meditation and self-inquiry. However, it is also a distinct spiritual path with its own unique teachings and practices.
Q: Can Atimarga be practiced without a teacher?
A: While it is possible to practice Atimarga without a teacher, it is generally recommended to seek guidance from an experienced practitioner or spiritual teacher. This can help ensure that the practices are performed correctly and safely, and can also provide valuable insights and guidance on the path.
Q: How can I learn more about Atimarga?
A: There are many resources available for those interested in learning more about Atimarga, including books, online courses, and spiritual retreats. It is also possible to seek guidance from an experienced practitioner or spiritual teacher.
Related Deities
Atimarga is a non-dualistic spiritual path that emphasizes the direct experience of the divine, rather than the worship of specific deities. However, some deities are associated with the practices and teachings of Atimarga. Here are a few examples:
Shiva: Shiva is a Hindu deity who is often associated with the practice of yoga and meditation. He is sometimes referred to as the Lord of Yoga and is revered as the ultimate reality or Brahman in Shaivism.
Vishnu: Vishnu is a Hindu deity who is often associated with devotion and selfless action. He is revered as the sustainer and preserver of the universe, and is often depicted holding a lotus flower, which symbolizes spiritual purity and detachment.
Kali: Kali is a Hindu goddess who is often associated with the destruction of the ego and the cultivation of inner strength and courage. She is revered as a fierce but compassionate deity who can help practitioners overcome obstacles and attain spiritual growth.
Tara: Tara is a Buddhist goddess who is often associated with compassion and wisdom. She is revered as a manifestation of the ultimate reality and can help practitioners overcome fear and confusion on the path to enlightenment.
Mahakala: Mahakala is a Hindu and Buddhist deity who is often associated with the destruction of ignorance and the cultivation of inner strength and courage. He is revered as a fierce but compassionate protector who can help practitioners overcome obstacles and attain spiritual growth.
It's important to note that while these deities are associated with Atimarga, they are not the focus of the practice. Rather, the emphasis is on the direct experience of the divine, which transcends any specific deity or religious tradition.
References
Conclusion
In conclusion, Atimarga is a non-dualistic spiritual path that emphasizes the direct experience of the divine, rather than adherence to specific religious practices or beliefs. The teachings of Atimarga can be found in a variety of Hindu and Buddhist scriptures, and the path is associated with deities such as Shiva, Vishnu, Kali, Tara, and Mahakala. While Atimarga is not as well-known as other spiritual paths, it offers a unique and powerful approach to self-realization and spiritual growth.
...